Periodic Systems: NoTerm-2022
HW 3 : Due Day 8 11/9
- Delta Function Well
S0 4501S
Consider a particle with mass \(m\) in a one dimension potential: \begin{align*} V(x) &= -\gamma\delta(x) \end{align*}
where \(\gamma\) is positive.
- Sketch a graph of the potential.
- What are the dimensions of the constant \(\gamma\)?
For this potential, there is only one bound state. Solve for the energy eigenstate and value of the energy of the bound state.
Hint: There are actually two approaches you can use to solve this. The first approach is to work with the \(\delta\) function directly and use the appropriate boundary conditions for an infinite potential. The second approach is to start with the solution to a finite square well and then turn it into a delta function well by taking the limit that the width of the well goes to zero.
- Sketch the wave function of the bound state.
- Qualitative Solutions for Bumpy Wells
S0 4501S
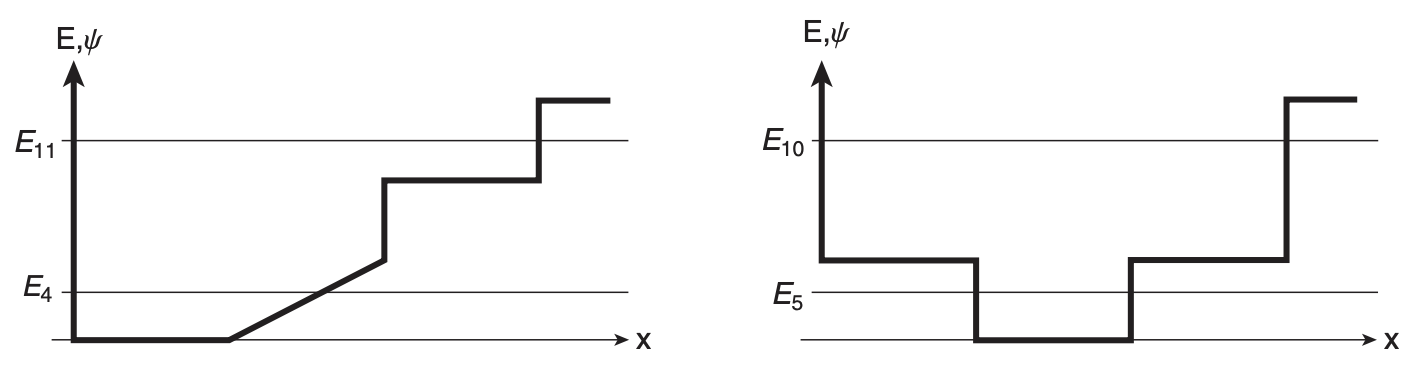
For each of the potential wells shown in the figure, make a qualitative sketch of the two energy eigenstate wave functions whose energies are indicated. For each energy state, identify the classically allowed and forbidden regions. Discuss the important qualitative features of each state.
- Fourier Transform of Cosine and Sine
S0 4501S
- Find the Fourier transforms of \(f(x)=\cos kx\) and \(g(x)=\sin kx\).
- Find the Fourier transform of \(g(x)\) using the formula for the Fourier transform of a derivative and your result for the Fourier transform of \(f(x)\). Compare with your previous answer.
- In quantum mechanics, the Fourier transform is the set of coefficients in the expansion of a quantum state in terms of plane waves, i.e. the function \(\tilde{f}(k)\) is a continuous histogram of how much each functions \(e^{ikx}\) contributes to the quantum state. What does the Fourier transform of the function \(\cos kx\) tell you about which plane waves make up this quantum state? Write a sentence or two about how this makes sense.