Oscillations and Waves: Winter-2026
HW 2a: Due W2 D3
- Inhomogeneous Linear ODEs with Constant Coefficients (First Example)
Inhomogeneous, linear ODEs with constant coefficients are among the most straigtforward to solve, although the algebra can get messy. This content should have been covered in your Differential Equations course (MTH 256 or equiv.). If you need a review, please see: The Method for Inhomogeneous Equations or your differential equations text.
The general solution of the homogeneous differential equation
\[\ddot{x}-\dot{x}-6 x=0\]
is
\[x(t)=A\, e^{3t}+ B\, e^{-2t}\]
where \(A\) and \(B\) are arbitrary constants that would be determined by the initial conditions of the problem.
Find a particular solution of the inhomogeneous differential equation \(\ddot{x}-\dot{x}-6 x=-25\sin(4 t)\).
Find the general solution of \(\ddot{x}-\dot{x}-6 x=-25\sin(4 t)\).
Some terms in your general solution have an undetermined coefficients, while some coefficients are fully determined. Explain what is different about these two cases.
Find a particular solution of \(\ddot{x}-\dot{x}-6 x=12 e^{-3 t}\)
Find the general solution of \(\ddot{x}-\dot{x}-6 x=12 e^{-3 t}-25\sin(4 t)\)
How is this general solution related to the particular solutions you found in the previous parts of this question?
Can you add these particular solutions together with arbitrary coefficients to get a new particular solution?
- Sense-making: Check your answer; Explicitly plug in your final answer in part (e) and check that it satisfies the differential equation.
- Shifted Sinusoids
A fun and fascinating fact about sinusoids is that a (normalized) sum of a cosine and a sine function is just a shifted cosine function. You can see this relationship geometrically using the Geogebra applet in https://books.physics.oregonstate.edu/GMM/fourierggb.html. Below is an algebraic proof:
For \(a\) and \(b\) related by the normalization condition \(a^2+b^2=1\), we have \begin{align} a\cos\theta+b\sin\theta &=a\, \frac{e^{i\theta}+e^{-i\theta}}{2} +b\, \frac{e^{i\theta}-e^{-i\theta}}{2i}\\ &=\frac{a-ib}{2}\, e^{i\theta} + \frac{a+ib}{2}\, e^{-i\theta}\\ &=\frac{1}{2} e^{-i\phi}\, e^{i\theta} + \frac{1}{2} e^{i\phi}\, e^{-i\theta}\\ &=\frac{1}{2} e^{i(\theta-\phi)} + \frac{1}{2} e^{-i(\theta-\phi)}\\ &=\cos(\theta-\phi) \end{align} where in (1) we have used Euler's formula, in (2) we have regrouped terms, in (3) we have rewritten \(a+ib=e^{i\phi}\), in (4) we have combined exponents, and in (5) we have used the inverse form of Euler's formulas.
In the rest of this class, we will discuss 4 different forms of the solutions of the equation of motion for a simple harmonic oscillator: \begin{align*} \mbox{A Form: } x(t) &= A\cos(\omega t + \phi) \\[12pt] \mbox{B Form: } x(t) &= B_1\cos(\omega t) + B_2\sin(\omega t)\\[12pt] \mbox{C Form: } x(t) &= Ce^{i\omega t} + C^*e^{-i\omega t}\\[12pt] \mbox{D Form: } x(t) &= Re[De^{i\omega t}] \end{align*}
- In the calculation above, identify lines of the calculation that represent the A, B, and C forms.
- From your identifications, find relationships between the constants in the A, B, and C forms.
- A Physical System that Oscillates
A mass \(m\) is strung on a very light wire equidistant between two anchor points separated by a distance \(2L\). When the mass is displaced laterally (i.e. plucked) in the \(x\)-direction (here vertically), there is constant tension \(T\) on the wire that produces a restoring force.
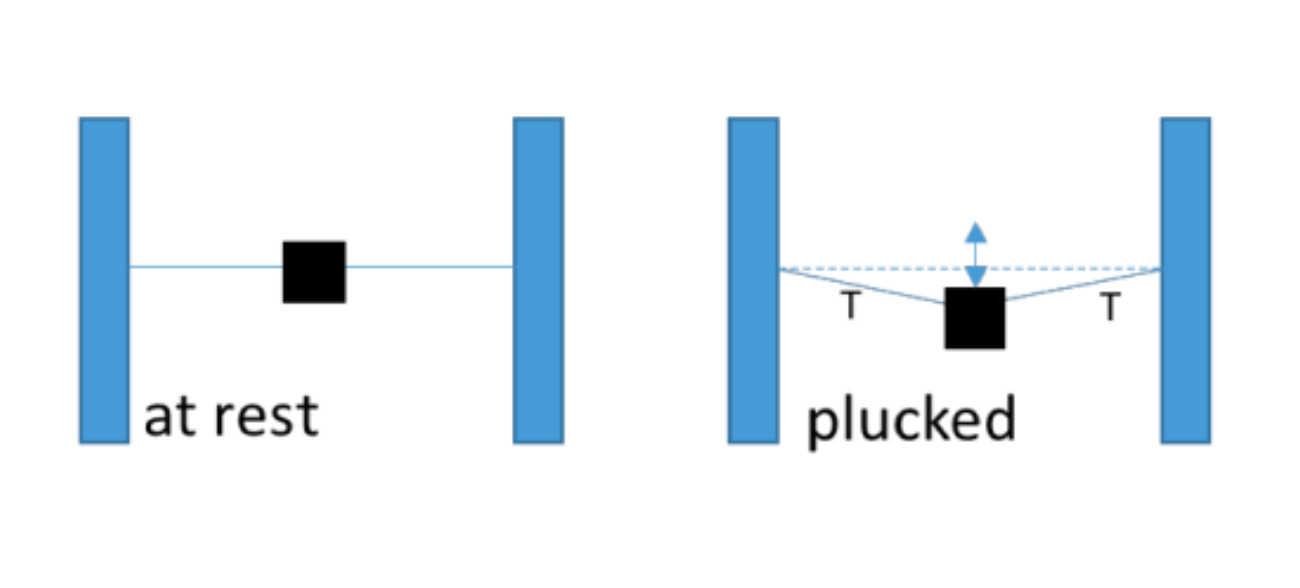
What is the resulting natural frequency \(\omega_0\) of the oscillating mass? Assume tension drives the oscillation (i.e. no gravity, if it helps pretend you are looking down at a mass resting on a frictionless surface) and assume the angle the string makes with the posts is small.
Note: \(\omega_0\) must be expressed in terms of the physical parameters given in the problem (\(T, L, m\)).
- Write a generic expression for displacement from equilibrium in any of the standard forms, \(ABCD\).