Non-dispersive Triangle Wave
-
Oscillations and Waves 2023
A banjo string (mass per unit length \(\mu\) under tension \(T\)) is anchored at \(x=0\) and \(x=L\). It is displaced so that it has the following profile at \(t=0\), and the transverse velocity at all points is zero at \(t=0\). (The diagram shows a vastly exaggerated displacement -- we assume that \(A<<L\) so that the string stretches only a little and its stretched length is only slightly larger than \(L\).)
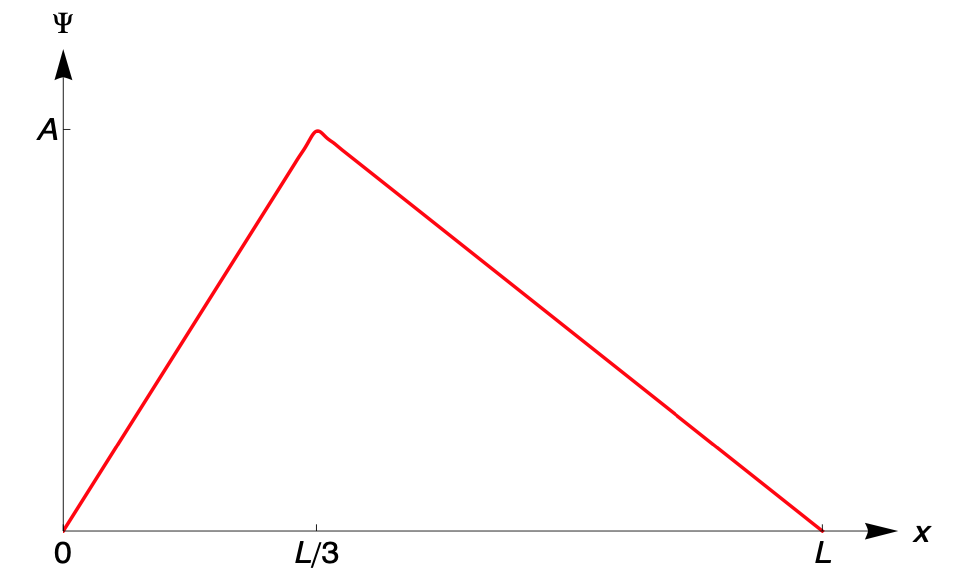
Write the wave form as a superposition of standing waves of all \(k\) values (and corresponding frequencies \(\omega_k=vk\)).
The information about the initial condition on the velocity eliminates a large number of coefficients. Which ones are zero and why?
The condition that the string is anchored at \(x=0\) eliminates more coefficients. Which ones are zero and why?
The condition that the string is anchored at \(x=L\) defines special values of \(k\) that are allowed in the sum. Define these special values \(k_n\) in terms of \(L\) and an integer variable \(n\). Rewrite the sum with all this information so that is is now a Fourier sum.
Use Fourier analysis to find the coefficients for this triangle wave at \(t=0\).
Now write the full \(\psi(x,t)\) making sure you connect the frequency in each term to the \(k\) value in each term. \[\psi(x,t)=\sum_nC_n\sin{(k_nx)}\cos{(\omega_nt)}\]
Animate the function! Does it do what you expect?
- Here we have use \(L/3\) for the peak of the wave. How would the sound of the banjo change if it was at L/2? Or L/9?